Laptops have become one of the most important gadgets for our daily life and for getting the best performance out of them you have to have sufficient amounts of laptop RAM. RAM is the acronym for Random Access Memory and it is the most essential part of your laptop that is responsible for its flawless and fast performance.
With the advancement in technology we have different types of laptop RAM and if you want to know how to select the right RAM you must know the Laptop RAM difference.
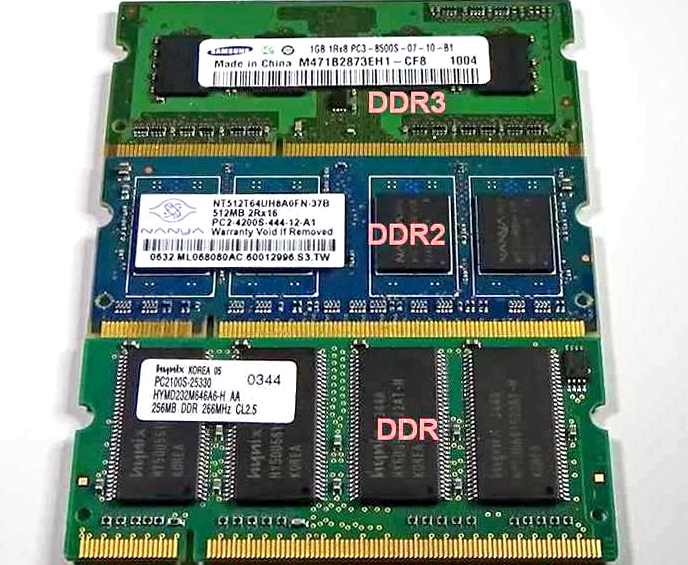
We have different varieties of RAM in our laptops and they can be of DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 or DDR4 types and they all come under the SDRAM category. When you want to know the Laptop RAM difference, you must understand that though all the four types of RAM do the same function in providing the memory support to your laptop during its operation they have some vital differences both in physical design and performance design.
Download Computer Troubleshooting Guide


You have to be aware of these to know exactly what you mean by each term and what it holds for your computer’s performance and how you can select the right one if you have to replace them and to avoid compatibility problems when doing so.
The RAM modules of the present days are built for faster operation, large volume of storage and function in a way to support the faster and stronger processors with which they are operating in your laptop. The most basic difference that exists between DDR1, DDR2 and DDR3 are the
- Number of pins
- Operating voltage
- Data transfer times and
- Frequency at which they are operating
- Position of the Notch on the module
When you study the laptop RAM difference you will appreciate that these are different for each of the RAM types and hence they are not compatible with each other and hence they cannot be mix and matched. RAM provides the facility to store the data both before and after processing on a temporary basis and is now available in different versions and speeds to match the performance specifications of the present day laptop computers.
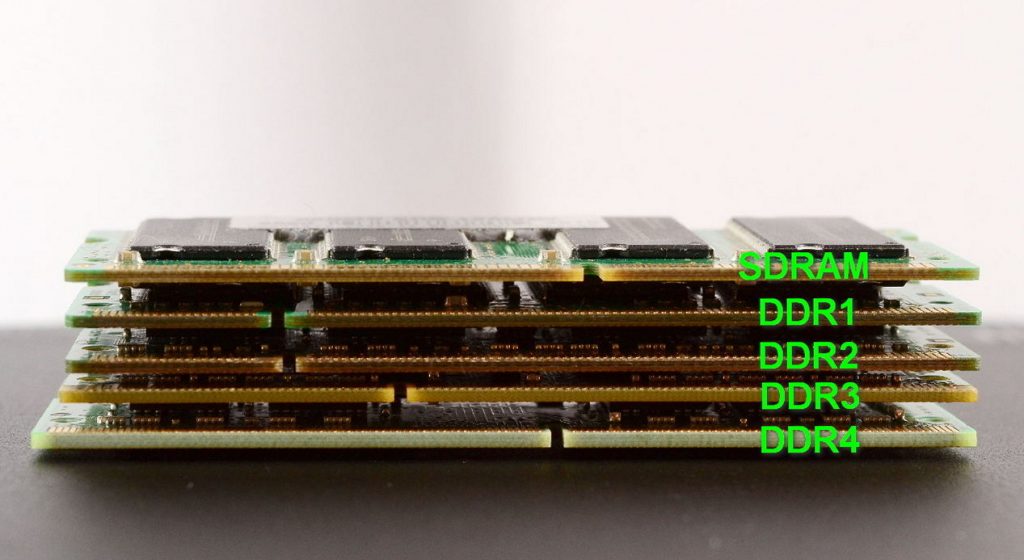
The present day RAM is built on the Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory using the Double Data Rate specifications and hence they are called as SDRAM of DDR1, DDR2, or DDR3 versions. They work on the basis of double pumping, dual pumping or double transition process. They are able to provide two data transfer for each clock cycle.
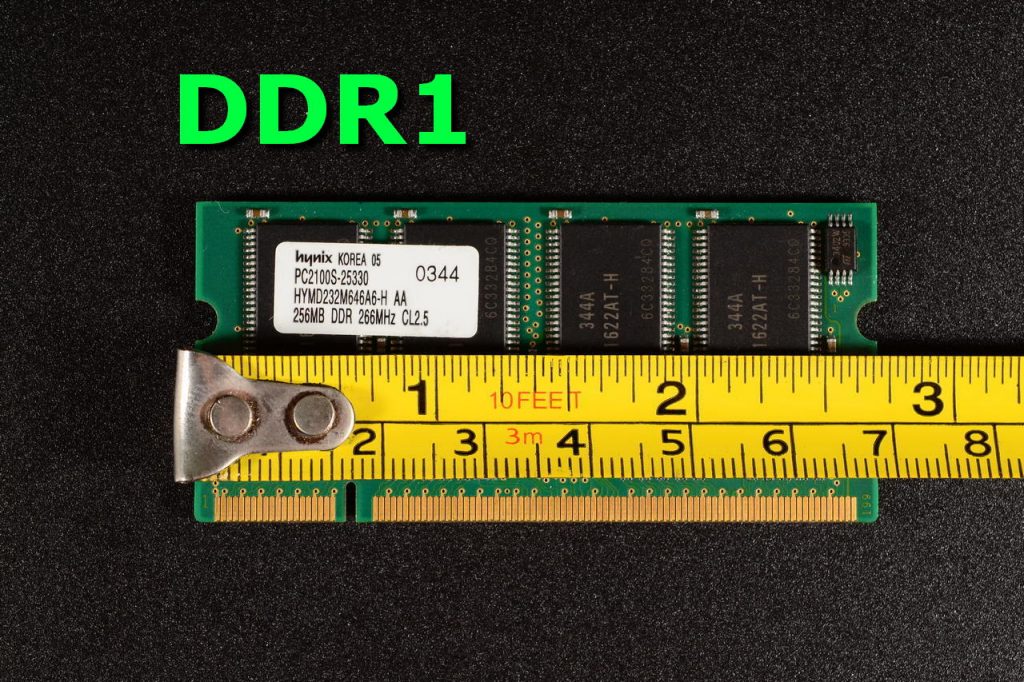
DDR1
The first in the category of RAM is the DDR or DDR1 RAM and it belongs to the first generation in the SDRAM technological evolution. It is characterized by enhanced prefetching, strobe based data bus, double transition clocking, low voltage signalling, Stub- series Terminated logic-2 etc. Comes with 184 pins and works at the highest voltage range.

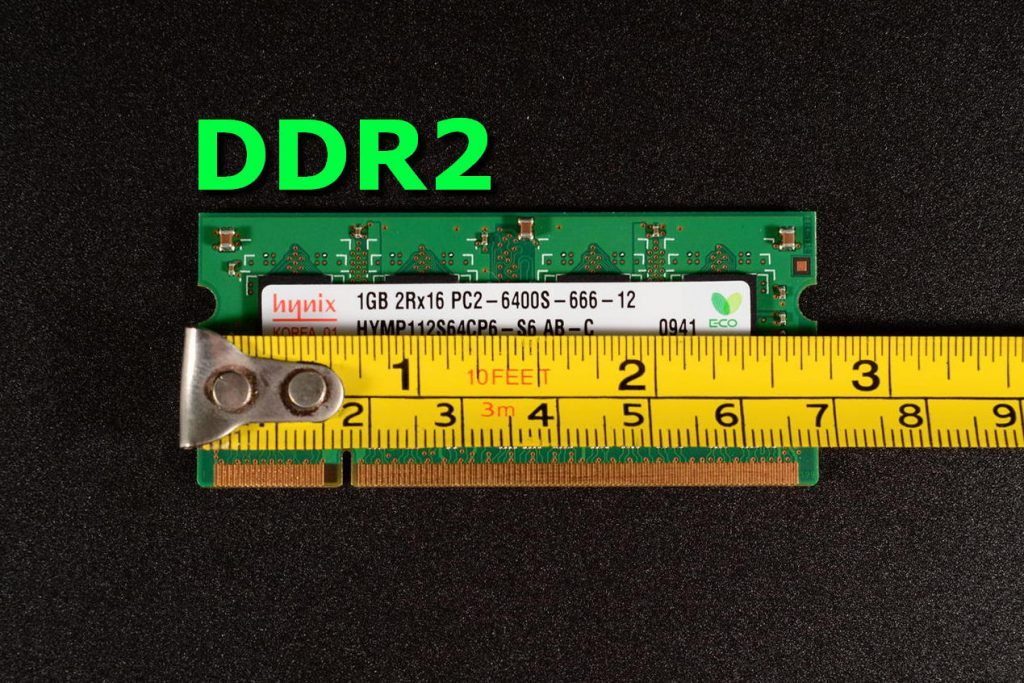
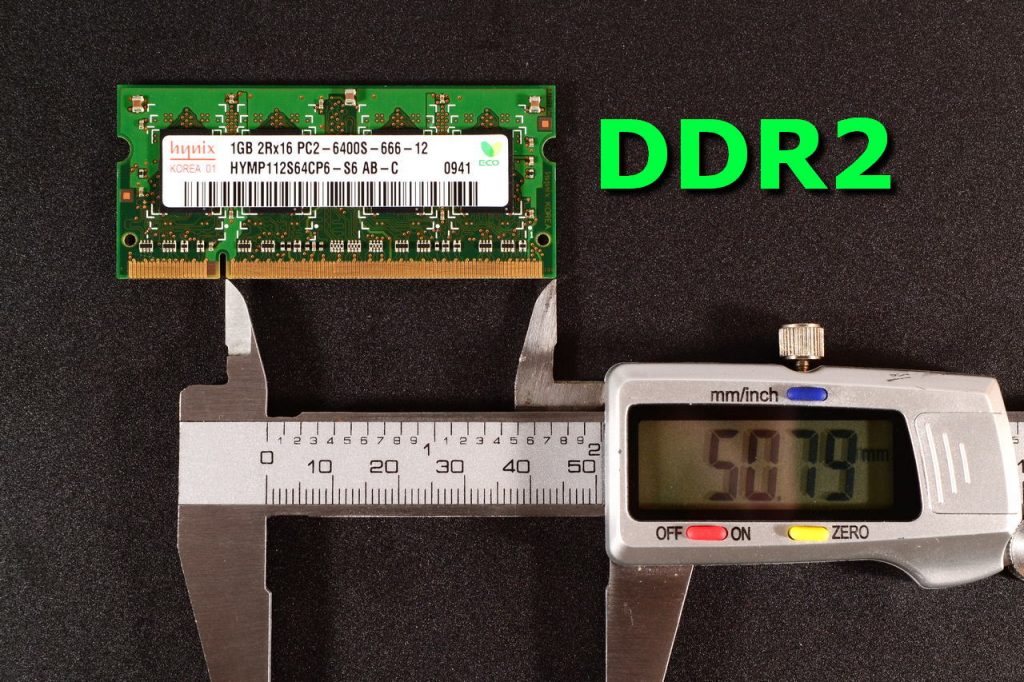
DDR2
DDR2 RAM is the successor of DDR1 and gives a data transfer rates of up to 6.4 GB per second and works at a lower voltage, and gives much improved performance than the DDR1 due to the faster clocks, low voltage ( 1.8 volts) operation, with a simplified command set is able to give better performance than the DDR1

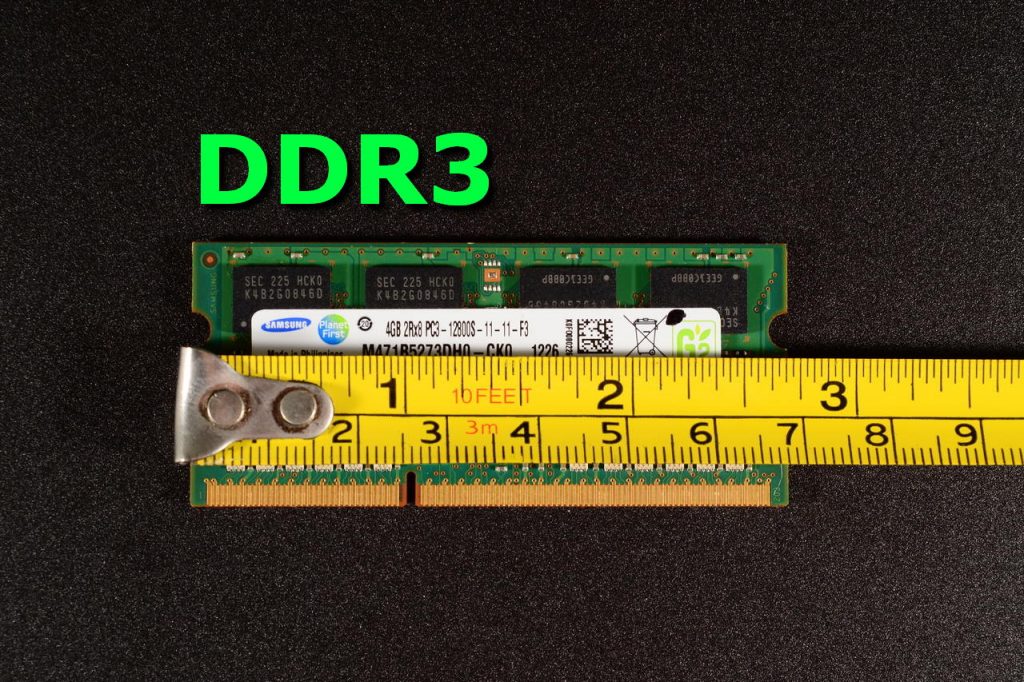
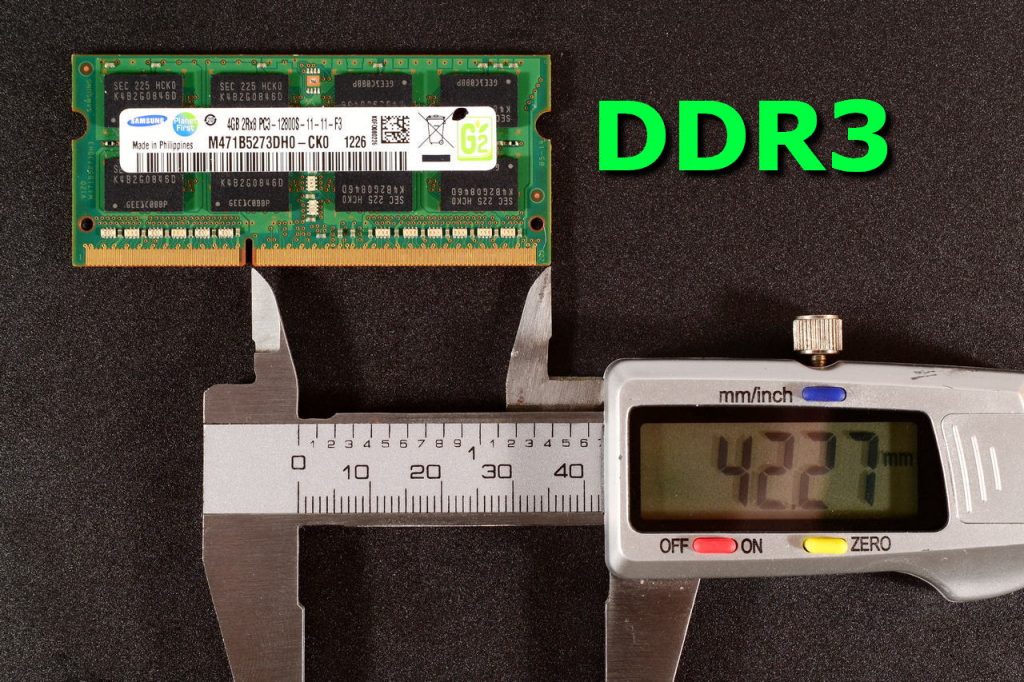
DDR3
While learning the laptop RAM difference you will find that the DDR3 belongs to the third generation of laptop RAM and is a further improved version over DDR2 as it has more improved data transfer bandwidth and still lower power consumption. The DDR3 RAM is designed to operate at 400MHz to 1066 MHz and can transfer from 6.40GB to 17 GB per second. DDR3 RAM design gives chip capacities of 512 MB to 16 GB.


Due to the continuous evolution and advancements in the computer memory technology the DDR1 has become obsolete and they are not mass produced anymore. Due to better performance and streamlined operation and compact size DDR3 and DDR4 are more preferred for use in the present days.
Laptop RAM comparison table
Please find below the laptop RAM difference and laptop RAM comparison table:
| DDR | DDR2 | DDR3 | DDR4 | |
| Voltage | Highest voltage | Lower than DDR but higher in comparison to DDR3. | Operates at low voltage. | Operates at lowest voltage. |
| Typical latency | 3 | 5 | 7 | 15 |
| Number of pins | 184 | 240 | 240 | 288 |
| Maximum Theoretical Transfer Rate (MB/s) | DDR200 -1600 DDR266 – 2133 DDR333 – 2666 DDR400 – 3200 | DDR2(400) – 3200 DDR2(533) – 4266 DDR2(667) – 5333 DDR2 (800) – 6400 DDR2(1066) – 8533 | DDR3(800) – 6400 DDR3(1066) – 8500 DDR3(1333) – 10666 DDR3(1600) – 12800 | DDR4-1600 (PC4-12800) DDR4-1866 (PC4-14900) DDR4-2133 (PC4-17000) DDR4-2400 (PC4-19200) DDR4-2666 (PC4-21333) DDR4-2933 (PC4-23466) DDR4-3200 (PC4-25600) |
| Bus Speed in MHz | DDR200 -100 DDR266 – 133 DDR333 – 166 DDR400 – 200 | DDR2(400) – 200 DDR2(533) – 266 DDR2(667) – 333 DDR2 (800) – 400 | DDR3(800) – 400 DDR3(1066) – 533 DDR3(1333) – 667 DDR3(1600) – 800 | DDR4-1600 – 800 DDR4-1866 – 933 DDR4-2133 – 1066 DDR4-2400 – 1200 DDR4-2666 – 1333 DDR4-2933 – 1466 DDR4-3200 – 1600 |
| Basic Features of the laptop RAM | • Prefetching – based on a 2n-prefetch architecture. • Double transition clocking – provides twice the bandwidth of SDRAM without the need of increasing the clock frequency. • Stub-Series Terminated Logic_2 (SSTL_2) low-voltage signaling technology – It uses e 2.5-V signaling specification SSTL_2. • Strobe-based data bus – Used for locating the data in a more accurate manner. | • Connector of 240 pins • Faster clocks • 1.8-V operation and signaling • A simplified command set | • An eight bit prefetch buffer stores more data than the 4-bit buffer of DDR2. • Fly-by topology for the commands, addresses, control signals, and clock to improve the integrity of signals. • 1.5-V signaling reduces power consumption from the 1.8- V signaling for DDR2. • A thermal sensor integrated on the DIMM module signals the chipset to throttle memory traffic. | The primary advantages of DDR4 over its predecessor, DDR3, include higher module density and lower voltage requirements, coupled with higher data rate transfer speeds. The DDR4 standard allows for DIMMs of up to 64 GiB in capacity, compared to DDR3’s maximum of 16 GiB per DIMM. |
| Packaging | Thin small-outline package | Ball Grid Array | Ball Grid Array | Ball Grid Array |
| Data Strobes | Single-ended | Single-ended or differential | Differential only | |
| Modules | 184-pin DIMM unbuffered registered; 200-pin SODIMM; 172-pin MicroDIMM | 240-pin DIMM unbuffered registered; 200-pin SODIMM; 214-pin MicroDIMM | 240-pin DIMM (same size as DDR2 but are electrically incompatible with DDR2 DIMMs and have a different key notch location). DDR3 SO-DIMMs have 204 pins. |
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.